Chapter 6b: Ideas for Midterm Projects
Midterm 1: Environmental Audits
Introduction
In the business world, an audit is a formal review of an organization’s systems, processes, or performance. Audits are essential tools for businesses that want to ensure they’re operating efficiently, ethically, legally—and in a way that meets the expectations of their customers, stakeholders, and the planet. Audits can be internal or external, and they often serve as the starting point for business decisions, sustainability efforts, and public communication strategies.
Internal Audits: A Tool for Improvement
An internal audit is a structured evaluation of a company’s internal operations (refer to chapter 1A for a review on internal communication). Its purpose is to identify risks, inefficiencies, or opportunities to improve the business. Companies often request internal audits to strengthen their operations, improve accountability, or prepare for sustainability certification.
Internal auditing examines and assesses company records, workflows, systems, and processes. They analyze company records and financial documents. Teams identify issues like complete risk assessments, investigate internal or external fraud, compliance concerns, and sometimes identify financial reporting inaccuracies. The audit team’s ultimate goal is to be a valued business partner for other members of the organization. [1]
Internal audits may cover:
- Operations and workflow efficiency
- Financial controls
- Compliance with laws and internal policies
- Environmental impact of business activities
- Company culture and ethical practices
- Product and service quality
In short, internal audits help companies figure out how to do better—from reducing waste and energy use to improving employee training and supply chain transparency. [2]
Real-World Example of an Internal Audit:
A clothing retailer might conduct an internal audit to review whether its “sustainable cotton” claims are supported by actual supplier documentation. If the audit reveals weak tracking systems, the company can fix them before facing public backlash for greenwashing.
External Audits: Building Public Trust
An external audit is conducted by an independent organization or regulatory body. It’s designed to verify claims, confirm compliance, or evaluate performance for an outside audience—such as investors, regulators, or the general public.
External audits are common in:
- Financial reporting (e.g., audited annual reports)
- Environmental compliance (e.g., emissions tracking)
- Sustainability certifications (e.g., LEED, B Corp, Fair Trade)
Because external audits come from a neutral source, they carry more credibility. A company that passes a rigorous external audit may use the results in its marketing, investor reports, or public sustainability claims.
Real-World Example of an External Audit
Patagonia undergoes third-party environmental audits to maintain its reputation as a sustainable brand. These audits verify the company’s supply chain practices and allow it to earn certifications that customers trust.
The Process of External Audits
A few essential procedures are usually followed by an external auditor, including:
- Working closely with your finance team to comprehend internal control systems, operations, and any particular risks or areas of concern is part of the planning and preparation process.
- Gathering and examining financial documents, records, and other pertinent data in order to evaluate the completeness and accuracy of your financial statements.
- Assessing the organization’s internal control systems’ efficacy and design in order to spot any flaws or potential areas for development.
- Conducting tests, such as analytical reviews and sampling, to confirm the accuracy and validity of the financial data is known as substantive testing.
- Drafting a report outlining their conclusions, any problems or inconsistencies, and suggestions for enhancements.
- Following up and remediating, resolving any issues or vulnerabilities found in the audit report and then taking any action necessary. [3]
Types of Business Audits Relevant to Sustainability
- Environmental Audit – Assesses how a company’s operations affect the environment (e.g., emissions, water use, waste).
- Operational Audit – Evaluates how efficiently and sustainably operations are run.
- Compliance Audit – Checks if the company is following environmental laws, regulations, and internal policies.
- Performance Audit – Measures whether sustainability goals or efficiency targets are being met.
- Financial Audit – Reviews accuracy of financial records; can include sustainability budgeting.
Environmental Audits
For the relevance of this textbook, we will focus specifically on environmental audits. Environmental audits are essential for businesses that want to become (and stay) environmentally responsible. These audits may also assess an organization’s compliance with environmental laws and regulations. With more boards, individual investors, and consumers focusing on ESG (environmental, social, and governance), this should be a high-priority area for an organization’s internal audit team.
Whether internal or external, environmental audits help companies:
- Avoid greenwashing by identifying gaps between their messaging and actual performance
- Reduce environmental risks by catching harmful or wasteful practices early
- Track progress toward goals like net-zero emissions or zero-waste production
- Communicate transparently with customers, regulators, and stakeholders
- Earn certifications that increase trust and marketability
Audit Process Overview
Audits typically follow these four steps:
- Planning – The company and auditors define the scope and goals of the audit. Risks and priorities are identified.
- Auditing – The audit team collects and reviews data. This may include surveys, employee interviews, documentation, or site inspections.
- Reporting – A report is written to share findings, identify issues, and recommend solutions.
- Monitoring – After the audit, companies track progress and may follow up with smaller audits to ensure improvements are made.
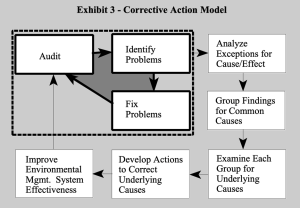
Below is a visual of how the EPA follows a corrective action model. This visual flowchart illustrates the steps businesses follow after conducting an audit, specifically focusing on identifying and correcting problems in order to improve environmental management system effectiveness. The diagram is organized into two connected sections, one on the left and one on the right.
Left Section: The Audit and Immediate Response Loop
This section is enclosed in a dashed-line box and shows a cyclical process that begins and ends with an audit.
- Audit
- This is the starting point. A business conducts an audit to examine its systems and practices.
- Identify Problems
- The audit results help uncover issues or areas of concern.
- Fix Problems
- Once identified, the company takes steps to correct or resolve the problems found.
- The cycle then loops back to the audit step, suggesting this is a repeating process of continuous improvement.
Right Section: Deeper Root Cause Analysis. This section details how to go beyond surface-level fixes and address underlying causes of problems:
- Analyze Exceptions for Cause/Effect
- After identifying problems, the company analyzes unusual or problematic events to understand their causes and consequences.
- Group Findings for Common Causes
- Similar problems are grouped together to detect patterns or systemic issues.
- Examine Each Group for Underlying Causes
- Each group is then reviewed more deeply to uncover root causes behind the problems.
- Develop Actions to Correct Underlying Causes
- Specific corrective actions are created to resolve the root causes and prevent recurrence.
Final Outcome: System Improvement. The process ultimately leads to the goal:
“Improve Environmental Management System Effectiveness”
This box is at the bottom left and connected to both the audit cycle and the corrective action analysis steps, showing that both surface fixes and deeper analysis contribute to long-term improvement.
The Institute of Internal Auditors (IAA) is a global guidance-setting body that provides the conceptual framework International Professional Practices Framework (IPPF). [5]
They describe the internal audit process as starting with a risk assessment to identify and prioritize potential high-risk areas, focusing on the most important auditable activities. An audit plan, which is a list of audits to be carried out, is created using the risk assessment. In order to establish the goals for the audit steps to be carried out, the audit team will scope the audit and conduct fieldwork, which requires understanding the current procedures and related risks. Following all of this, teams draft an official audit report that they distribute to the audit committee, senior management, and line management. Finally, to ensure that plans are carried out, teams follow up on all audit recommendations and management corrective action plans. They recommend readers to look outside of their company and gain knowledge from people who have gone through similar experiences and projects when creating a system for a group or task. [6]
Evaluating Audit Reports
5 Cs of Audit Reports
Audit reports tend to follow the 5 Cs for effectiveness:
- Criteria – What was evaluated and why?
- Condition – What did the audit observe?
- Cause – Why did these issues occur?
- Consequence – What impact do the issues have?
- Corrective Action – What can be done to fix them? [7]
Environmental Audit Clause
Here’s how a clause might appear in a contract or policy:
“The Company agrees to conduct an annual environmental audit to assess its operations for compliance with applicable environmental laws and regulations. The audit will evaluate energy usage, waste management practices, and carbon emissions, and provide recommendations for improvements. The results of the audit will be reported to senior management and regulatory authorities if required.” [8]
Why Audits Matter
Audits don’t just lead to improvements; they also shape how businesses communicate with the public. That’s why business communicators must understand audits, not just as data tools, but as stories that inform branding, reputation, and stakeholder trust.
Discussion Questions
- What is the difference between an internal and an external audit?
- Why do businesses need both an internal an external environmental audit?
- Why might a company conduct an internal environmental audit before launching a sustainability marketing campaign?
- How do communication professionals “translate” audit findings for the public?
- How can an environmental audit help prevent greenwashing?
- Think of a company you admire or one discussed previously in this course. What kind of audit would be most useful for improving its environmental performance?
- What are the benefits of using third-party auditors versus conducting audits internally?
- What are the risks for a business that avoids or delays audits of its environmental practices?
- What kind of information would you expect to see in an environmental audit report summary? Why is that useful for the public or investors?
- Based on previous discussions or your own experience, where can individuals find reliable information about a company’s environmental practices if they wanted to prepare an environmental audit?
Midterm Activities for Option 1
Midterm 1a: Mini-Audit of a Campus or Local Business
Objective: Apply audit principles by observing and analyzing the sustainability practices of a real-world location.
Instructions:
- In a group, discuss where you work or have worked, such as a small campus unit (e.g., coffee shop, bookstore) or local business.
- Discuss the company’s operations such as energy use, waste disposal, packaging, etc.
- Identify 2–3 possible sustainability issues that could be better (e.g., plastic use, lighting).
- Share your point of view with the class in a short summary.
Midterm 1b: Environmental Audit Comparison Brief
Objective: Analyze how different companies use audits to communicate sustainability; explore and evaluate a real-world environmental audit to better understand how businesses assess and communicate their sustainability performance.
Instructions:
- Choose two companies in the same industry (e.g., fashion, food, tech). It can be a publicly available environmental audit or sustainability report from a real company (e.g., Patagonia, Unilever, IKEA).
- Find and compare any publicly available audit-related documents (e.g., sustainability reports, certifications).
- Read the audit(s) and take notes on what the report(s) evaluate and how they are presented.
- Write a 500-word comparative brief:
- What kind of audits do they reference?
- How do they communicate findings?
- Which company appears more transparent or credible?
- In a short reflection (300–400 words), respond to the following:
- What did you learn from this audit?
- What information surprised you or caught your attention?
- Was there anything you didn’t understand?
- Do you have any questions about how the audit was conducted or reported?
- Prepare to share your findings and reflections in a small group or class discussion. If you analyzed the same companies or reports, compare and contrast your answers to 3 and 5 above.
Midterm 1c: Memo Recommending Improvements Based on Audit and Communication Principles
Objective: Synthesize your understanding of audits and business communication by writing a professional memo that recommends realistic improvements tied to key course concepts such as greenwashing, credibility, transparency, and SMART goals.
Instructions:
- Choose a real or fictional company.
- Imagine you are writing a memo to this company’s Sustainability Director.
- Identify 2–3 sustainability-related challenges or areas for improvement. These can be based on a previous audit, activity one above, course readings, or your own observations.
- Write a 300–500 word memo that:
- Describes the current situation or challenges clearly and concisely
- Highlights why these issues matter (consider risks of greenwashing, lack of credibility, etc.)
- Proposes SMART recommendations (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) for addressing the issues (see 1B for more info)
- Emphasizes the value of transparency and communication with stakeholders
- Find a memo template in Word (new, new from template, search for “memo”) or online. Write a short letter, similar to an email, but memos are usually printed and distributed internally.
Memo Template:
MEMO
To: [Sustainability Director’s Name]
From: [Your Name]
Date: [Insert Date]
Subject: Recommendations to Improve [Insert Company Name]’s Environmental Communication
Introduction: Briefly describe the purpose of the memo.
Observations: Identify 2–3 key areas of concern.
Analysis: Discuss the relevance of these issues, referencing greenwashing risks, stakeholder trust, or previous audit insights.
Recommendations: Offer clear, SMART recommendations for improvement.
Conclusion: Summarize the benefits of implementing your suggestions.
Memo Example:
MEMO
To: Maria Fernandez, Sustainability Director
From: Jordan Lee
Date: October 3, 2025
Subject: Recommendations to Improve FreshBrew Café’s Environmental Communication
This memo outlines several opportunities for FreshBrew Café to strengthen its environmental practices and improve the credibility of its sustainability messaging. These suggestions are based on informal observations and principles discussed in a college course I am taking.
While FreshBrew Café promotes itself as an eco-conscious brand, there are notable gaps in its current practices. First, the café markets its cups as “eco-friendly,” yet there is no visible certification or clear labeling explaining their material or recyclability. Furthermore, the waste sorting bins are inconsistently labeled, and compostable options are not available. Lastly, the website highlights sustainability values but lacks concrete data or updates on goals or progress.
These gaps could lead to accusations of greenwashing, especially when environmental claims are made without proof. Consumers today are more informed and expect transparency. Without credible third-party certifications or measurable sustainability commitments, FreshBrew may risk losing stakeholder trust.
Recommendations
To improve transparency and accountability, I recommend the following:
- Partner with a certified supplier and clearly label all compostable or recyclable products by the end of Q2.
- Conduct a mini internal audit of waste practices with employee input by the end of this semester.
- Launch a public-facing “Green Progress” webpage with quarterly updates on sustainability efforts.
- Implement improved waste signage and compost bin placement across all café locations by January 15, 2026.
Conclusion
These small but strategic improvements can help FreshBrew Café avoid greenwashing claims, improve operational sustainability, and enhance its reputation as a transparent and environmentally responsible business.
Rubric
(10 points total):
| Criteria | Excellent (5) | Satisfactory (3–4) | Needs Improvement (1–2) |
| Content Accuracy | Clearly explains relevant concepts (audit, greenwashing, SMART goals) | Includes most relevant concepts with minor confusion | Lacks clarity or misuses key terms |
| Recommendations | SMART, realistic, and well-connected to analysis | Mostly clear and logical recommendations | Vague, unrealistic, or not actionable |
| Memo Structure & Tone | Follows memo format; professional and concise | Minor issues in format or tone | Disorganized or informal language |
| Grammar & Mechanics | Virtually no errors | Some minor errors | Frequent or distracting errors |
| Critical Thinking | Insightful connections between audit findings, risks, and communication strategies | Basic analysis of issues and risks | Limited analysis or critical insight |
Midterm 2: Recommendations-Based Report Midterm Assignments
Midterm 2a: Recommendations-Based Report
Objectives: Critically evaluate a company’s current communication methods regarding their sustainability initiatives; develop well-researched and actionable recommendations to enhance the effectiveness of these communications; apply principles of effective communication to promote sustainability within a business context; create a professional report that clearly articulates recommendations and their expected impact.
Instructions:
- Select a Company and Communication Method:
- Choose a company that has publicly shared its sustainability initiatives.
- Select one of their communication methods to evaluate, such as their website, a flyer, a social media campaign, or other promotional material.
- Focus Area:
- Decide whether your report will focus on one element of environmental sustainability (e.g., fashion, energy, water, waste) or multiple elements.
- Research:
- Conduct thorough research on best practices in communicating sustainability within the chosen focus area(s).
- Gather information on how other leading companies successfully communicate their sustainability initiatives.
- Start with resources from this textbook in the footnotes or see your business librarian and/or communication center and/or writing center for assistance.
- Evaluate the Current Communication:
- Analyze the selected communication method.
- Identify strengths and weaknesses in the current approach.
- Consider aspects such as clarity, transparency, engagement, visual appeal, and alignment with sustainability goals.
- Develop Recommendations:
- Based on your evaluation and research, develop a set of recommendations to improve the company’s communication about their sustainability initiatives.
- Ensure your recommendations are specific, actionable, and supported by evidence or best practices.
- Write Your Report:
-
- Use the provided template to structure your report.
- Make sure to include an executive summary, an introduction, a detailed evaluation, recommendations, and a conclusion.
- Submit Your Report:
- Submit your completed report by [due date].
Template for Recommendations-Based Report
Title Page
- Title: Recommendations for Enhancing Sustainability Communication
- Your Name
- Course Name
- Date
Executive Summary
- Brief overview of the company and the communication method evaluated.
- Summary of key findings and recommendations.
Introduction
- Introduction to the company and its sustainability initiatives.
- Purpose of the report and the selected communication method.
Evaluation of Current Communication
- Detailed analysis of the current communication method.
- Points supported with research (APA).
- Strengths and weaknesses identified.
Recommendations
- Recommendation 1: [Title]
- Description of the recommendation.
- Justification and supporting evidence.
- Expected impact.
- Recommendation 2: [Title]
- Description of the recommendation.
- Justification and supporting evidence.
- Expected impact.
- (Include additional recommendations as needed)
Conclusion
- Recap of key findings and recommendations.
- Final thoughts on the importance of effective sustainability communication.
References
- List of sources used in your research.
Example of Recommendations-Based Report
Title Page
Title: Recommendations for Enhancing Sustainability Communication
Jane Doe
Communicating Business Sustainability
March 20, 2026
Executive Summary This report evaluates the sustainability section of XYZ Company’s website. While the site provides comprehensive information, it lacks engagement and visual appeal. Key recommendations include incorporating interactive content, enhancing visual design, and improving transparency about sustainability goals and progress.
Introduction XYZ Company is committed to sustainability through various initiatives, including reducing carbon emissions, conserving water, and promoting ethical sourcing. This report evaluates the sustainability section of their website and provides recommendations to enhance communication effectiveness (Parenthetical citation, year).
Evaluation of Current Communication The sustainability section of XYZ Company’s website provides detailed information about their initiatives. However, the content is text-heavy, and the visual design is not engaging. The current approach lacks interactive elements that could better engage visitors and convey the company’s commitment to sustainability (“Title if no author,” n.d.).
Recommendations
- Interactive Content:
- Incorporate interactive elements such as infographics, videos, and quizzes to engage visitors.
- Justification: Interactive content can make complex information more accessible and engaging.
- Expected Impact: Increased visitor engagement and better understanding of sustainability initiatives.
- Enhanced Visual Design:
- Improve the visual appeal by using high-quality images, consistent branding, and an intuitive layout.
- Justification: A visually appealing design can capture visitors’ attention and make the information more digestible.
- Expected Impact: Improved user experience and retention of information.
- Improved Transparency:
- Provide regular updates on sustainability goals and progress through a dedicated section or blog.
- Justification: Transparency builds trust with stakeholders and demonstrates accountability.
- Expected Impact: Increased stakeholder trust and credibility.
Conclusion
Effective communication of sustainability initiatives is crucial for building trust and engagement with stakeholders. By incorporating interactive content, enhancing visual design, and improving transparency, XYZ Company can significantly improve the impact of their sustainability communication.
References
- Include all sources cited in your report.
Grading Rubric
| Criteria | Excellent (5) | Good (4) | Adequate (3) | Needs Improvement (2) | Poor (1) | Score |
| Executive Summary | Clear, concise, and engaging overview of the report. | Clear overview of the report. | Adequate overview but lacks engagement. | Incomplete or unclear overview. | No clear overview. | |
| Introduction | Clearly introduces the company, sustainability initiatives, and purpose of the report. | Introduces the company and purpose clearly. | Adequate introduction but lacks detail. | Introduction is incomplete or unclear. | No clear introduction. | |
| Evaluation | Thorough and insightful analysis of current communication supported by APA research. | Good analysis with clear strengths and weaknesses. Some research presented. | Adequate analysis but lacks depth or citations or references page. | Incomplete or unclear analysis without citations. | No clear analysis provided, no citations. | |
| Recommendations | Specific, actionable, and well-supported recommendations with clear impact. | Good recommendations with justification and impact. | Adequate recommendations but lacks detail. | Recommendations are unclear or lack support. | No clear recommendations provided. | |
| Conclusion | Clear and compelling summary of findings and recommendations. | Clear summary of findings and recommendations. | Adequate summary but lacks engagement. | Conclusion is unclear or lacks detail. | No clear conclusion. | |
| Mechanics | Professional, well-organized, and free of grammatical errors. | Well-organized and professional. Some tone sounded robotic. | Clear presentation but with minor errors. | Presentation is unclear or unprofessional. | Poor presentation quality or too much AI. |
Total Score: ____ / 30
Submission Details:
Submit your completed report by [due date].
Midterm 2b: Presentation of Recommendations-Based Report on Communicating Business Sustainability
Objective: Effectively present their evaluation and recommendations for enhancing a company’s sustainability communication; communicate complex ideas clearly and persuasively in a professional setting; utilize visual aids to support their presentation and engage the audience; respond confidently to questions and feedback from peers and instructors.
Instructions:
- Prepare Your Presentation:
- Based on your written recommendations report, create a presentation that summarizes your findings and recommendations.
- Use PowerPoint, Google Slides, or another presentation software to create visual aids that support your key points.
- Presentation Structure:
- Introduction: Introduce yourself and provide an overview of your presentation.
- Company Background: Briefly introduce the company and its sustainability initiatives.
- Problem Statement: Clearly define the communication problem you identified.
- Evaluation of Current Communication: Summarize your analysis of the current communication method.
- Recommendations: Present your recommendations in a clear and structured manner.
- Conclusion: Recap the key points and make a compelling case for your recommendations.
- Q&A: Be prepared to answer questions from the audience.
- Create Visual Aids:
- Include images, graphs, charts, and other visual elements to enhance your presentation.
- Ensure your slides are clear, professional, and visually engaging.
- Practice Your Presentation:
- Rehearse your presentation to ensure it fits within the allotted time (10-15 minutes).
- Focus on clear articulation, engaging delivery, and confident body language.
- Deliver Your Presentation:
- Each student/team will deliver their presentation in class on [presentation date].
- Dress professionally and use appropriate body language and eye contact.
- Engage the audience and be prepared to handle questions during the Q&A session.
Presentation Outline
Slide 1: Title Slide
- Title: Recommendations for Enhancing Sustainability Communication
- Your Name
- Course Name
- Date
Slide 2: Introduction
- Grab the audience’s attention such as with a quote, statistic, story, etc.
- Connect the attention-getter to your overview statement.
- Brief introduction of yourself and an overview of the presentation.
Slide 3: Company Background
- Briefly introduce the company and its sustainability initiatives.
Slide 4: Problem Statement
- Clearly define the communication problem you identified.
- Include relevant data or statistics to support the existence of the problem.
Slide 5: Evaluation of Current Communication
- Summarize your analysis of the current communication method.
- Highlight strengths and weaknesses.
Slide 6-8: Recommendations
- Present each recommendation on a separate slide.
- For each recommendation:
- Title of the recommendation.
- Description of the recommendation.
- Justification and supporting evidence.
- Expected impact.
Slide 9: Conclusion
- Recap the key points of your presentation.
- Make a compelling case for your recommendations.
Slide 10: Q&A
- “Thank you! We are now open to questions.”
- Include a “Thank You” slide with a prompt for questions.
Grading Rubric
| Criteria | Excellent (5) | Good (4) | Adequate (3) | Needs Improvement (2) | Poor (1) | Score |
| Introduction | Clear, engaging, and professional introduction. | Clear and professional introduction. | Adequate introduction but lacks engagement. | Incomplete or unclear introduction. | No clear introduction. | |
| Company Background | Provides a clear and concise background of the company and its sustainability initiatives. | Provides a good background but lacks some detail. | Adequate background but lacks engagement. | Incomplete or unclear background. | No clear background provided. | |
| Problem Statement | Clearly defines the problem with strong evidence. | Defines the problem with good evidence. | Defines the problem but lacks strong evidence. | Problem statement is unclear or lacks evidence. | No clear problem statement. | |
| Evaluation of Communication | Thorough and insightful analysis of current communication supported with research. | Good analysis with clear strengths and weaknesses. Could use more research. | Adequate analysis but lacks depth. Little or no research shown. | Incomplete or unclear analysis. | No clear analysis provided. | |
| Recommendations | Specific, actionable, and well-supported recommendations with clear impact. | Good recommendations with justification and impact. | Adequate recommendations but lacks detail. | Recommendations are unclear or lack support. | No clear recommendations provided. | |
| Conclusion | Clear and compelling summary of findings and recommendations. | Clear summary of findings and recommendations. | Adequate summary but lacks engagement. | Conclusion is unclear or lacks detail. | No clear conclusion. | |
| Q&A Session | Answers questions clearly and thoroughly, shows deep understanding. | Answers questions clearly, shows good understanding. | Adequate answers to questions, some understanding. | Incomplete or unclear answers, limited understanding. | Cannot answer questions, lacks understanding. | |
| Overall Presentation | Professional, engaging, clear speech, excellent body language. | Professional and clear, good engagement and body language. | Clear presentation but lacks engagement or professionalism. | Unclear or unprofessional delivery, needs improvement. | Poor delivery, very unclear or unprofessional. | |
| Visual Aids | Excellent use of visuals, clear, relevant, and professional. | Good use of visuals, mostly clear and relevant. | Adequate use of visuals, some relevance issues. | Limited or unclear visuals, not very relevant. | No or poor use of visuals. |
Total Score: ____ / 45
Submission Details:
- Submit your presentation slides by [due date].
- Be prepared to deliver your presentation in class on [presentation date].
Midterm 3: Grant Proposals
Midterm Assignment 3a: Writing a Grant Proposal for Business Sustainability Initiatives
Objectives: Research and identify potential funding sources for sustainability projects; develop a comprehensive and persuasive grant proposal to secure funding for a sustainability initiative; apply principles of effective writing and communication to clearly articulate project goals, methods, and expected outcomes; demonstrate an understanding of the components of a grant proposal, including problem statements, objectives, budget, and evaluation plans.
Instructions:
- Identify a Grant Opportunity:
- Research and select a grant opportunity relevant to business sustainability.
- The grant could be from a government agency, non-profit organization, foundation, or private entity.
- Ensure the grant aligns with the sustainability goals and initiatives of a company or hypothetical project you are interested in.
- Develop a Sustainability Initiative:
- Define a specific sustainability project or initiative that requires funding.
- The project could focus on areas such as renewable energy, waste reduction, water conservation, sustainable sourcing, or any other relevant sustainability aspect.
- Research:
- Conduct thorough research on the sustainability issue your project aims to address.
- Gather data and evidence to support the need for the project.
- Review best practices and case studies of similar successful projects.
- Write the Grant Proposal:
- Use the provided template to structure your proposal.
- Include all necessary sections: Cover Letter, Executive Summary, Introduction/Background, Problem Statement, Project Objectives, Project Methods/Design, Budget, Evaluation Plan, and Conclusion.
- Submit Your Proposal:
- Submit your completed grant proposal by [due date].
Template for Grant Proposal
Cover Letter
- Address the grant provider and briefly introduce your project.
- Include your contact information and express appreciation for the opportunity to apply.
Executive Summary
- Provide a concise overview of the project, including the problem, proposed solution, objectives, and expected outcomes.
Introduction/Background
- Introduce the company or organization and its commitment to sustainability.
- Provide context and background information on the sustainability issue being addressed.
Problem Statement
- Clearly define the problem your project aims to solve.
- Support your statement with data, statistics, and research findings.
Project Objectives
- List the specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives of the project.
Project Methods/Design
- Describe the methods and activities that will be used to achieve the project objectives.
- Include a timeline and key milestones.
Budget
- Provide a detailed budget outlining the costs associated with the project.
- Justify the need for each budget item and explain how the funds will be used effectively.
Evaluation Plan
- Explain how the success of the project will be measured and evaluated.
- Include specific metrics and methods for tracking progress and outcomes.
Conclusion
- Summarize the key points of the proposal and restate the importance of the project.
- Emphasize the potential impact and benefits of the project if funded.
References
- List all sources used in your research and proposal.
Example Grant Proposal
Cover Letter
[Your Name]
[Your Title]
[Your Organization]
[Address]
[City, State, ZIP Code]
[Email Address]
[Date]
[Grant Provider’s Name]
[Title]
[Organization]
[Address]
[City, State, ZIP Code]
Dear [Grant Provider’s Name],
I am writing to submit our grant proposal for [Project Title], a sustainability initiative aimed at [briefly describe the project]. We are excited about the opportunity to collaborate with [Grant Provider’s Organization] to achieve our sustainability goals and make a significant impact in our community. Thank you for considering our application.
Sincerely,
[Your Name]
Executive Summary
This proposal outlines [Company Name]’s plan to implement a comprehensive waste reduction program, targeting a 50% reduction in landfill waste over the next two years. By introducing advanced recycling systems, employee education programs, and sustainable procurement policies, we aim to significantly minimize our environmental footprint and set a benchmark for sustainability in our industry.
Introduction/Background
[Company Name] is committed to leading the way in sustainability within the [industry] sector. Our past initiatives have focused on reducing energy consumption and water usage, achieving significant milestones. This proposal seeks to address the critical issue of waste management, a growing concern for both our company and the broader community.
Problem Statement
The [industry] sector generates substantial waste, contributing to environmental degradation and resource depletion. Currently, [Company Name] sends approximately [X tons] of waste to landfills annually. This not only impacts the environment but also incurs significant costs. Our project aims to reduce landfill waste by 50%, demonstrating our commitment to sustainable business practices.
Project Objectives
- Implement advanced recycling systems to increase the recycling rate by 60% within one year.
- Launch an employee education program to promote waste reduction and recycling best practices.
- Establish sustainable procurement policies to minimize waste generation from the source.
Project Methods/Design
- Recycling Systems: Install state-of-the-art recycling bins and sorting stations throughout our facilities.
- Timeline: Months 1-3
- Employee Education: Develop and conduct training sessions and workshops for all employees.
- Timeline: Months 4-6
- Sustainable Procurement: Collaborate with suppliers to adopt sustainable packaging and materials.
- Timeline: Months 6-12
Budget
- Recycling Systems: $20,000
- Employee Education Program: $10,000
- Sustainable Procurement Initiatives: $15,000
- Total: $45,000
Evaluation Plan
- Track recycling rates monthly to measure progress.
- Conduct employee surveys to assess the effectiveness of the education program.
- Monitor procurement practices and waste generation rates.
Conclusion
Funding for this project will enable [Company Name] to significantly reduce its environmental impact, promote sustainability within our industry, and contribute to a healthier planet. We are confident that our comprehensive waste reduction program will serve as a model for other companies and yield substantial environmental and economic benefits.
References
- Include all sources cited in your proposal.
Grading Rubric
| Criteria | Excellent (5) | Good (4) | Adequate (3) | Needs Improvement (2) | Poor (1) | Score |
| Cover Letter | Clear, concise, and engaging | Clear and professional | Adequate but lacks engagement | Incomplete or unclear | No clear cover letter | |
| Executive Summary | Comprehensive and compelling | Clear overview | Adequate summary but lacks depth | Incomplete or unclear | No clear summary | |
| Introduction/Background | Thorough and well-researched | Good background information | Adequate background but lacks detail | Incomplete or unclear background | No clear background | |
| Problem Statement | Clearly defined with strong evidence | Defined with good evidence | Defined but lacks strong evidence | Unclear or lacks evidence | No clear problem statement | |
| Project Objectives | Specific, measurable, and achievable | Clear and relevant | Adequate but lacks specificity | Unclear or unrealistic objectives | No clear objectives | |
| Project Methods/Design | Detailed and well-structured | Good methods with clear steps | Adequate methods but lacks detail | Unclear or incomplete methods | No clear methods | |
| Budget | Detailed and justified | Clear and reasonable | Adequate but lacks justification | Unclear or unrealistic budget | No clear budget | |
| Evaluation Plan | Specific metrics and methods for tracking progress | Clear evaluation plan | Adequate but lacks specificity | Unclear or incomplete evaluation plan | No clear evaluation plan | |
| Conclusion | Compelling and concise | Clear summary and call to action | Adequate summary but lacks engagement | Incomplete or unclear | No clear conclusion | |
| Mechanics | Professional, well-organized, free of grammatical errors | Well-organized and professional | Clear but with minor errors | Unclear or unprofessional | Poor presentation quality | |
| Total Score: ____ / 50 |
Submission Details
- Submit your completed grant proposal by [due date].
- Be prepared to present a brief overview of your proposal in class on [presentation date].
Midterm Assignment 3b: Presenting Your Grant Proposal for Business Sustainability Initiatives
Objective: Effectively present their grant proposal for a sustainability initiative, demonstrating clear and persuasive communication; communicate complex ideas clearly and professionally in a public speaking setting; utilize visual aids to support their presentation and engage the audience; respond confidently to questions and feedback from peers and instructors.
Instructions:
- Prepare Your Presentation:
- Based on your written grant proposal, create a presentation that summarizes your project, objectives, methods, budget, and evaluation plan.
- Use PowerPoint, Google Slides, or another presentation software to create visual aids that support your key points.
- Presentation Structure:
- Introduction: Introduce yourself and provide an overview of your presentation.
- Project Background: Briefly introduce the company or organization and its commitment to sustainability.
- Problem Statement: Clearly define the sustainability issue your project addresses.
- Project Objectives and Methods: Summarize your project’s objectives and the methods you will use to achieve them.
- Budget: Present a summary of your budget, highlighting key expenses and justifications.
- Evaluation Plan: Describe how you will measure the success of your project.
- Conclusion: Recap the key points and make a compelling case for your project.
- Q&A: Be prepared to answer questions from the audience.
- Create Visual Aids:
- Include images, graphs, charts, and other visual elements to enhance your presentation.
- Ensure your slides are clear, professional, and visually engaging.
- Practice Your Presentation:
- Rehearse your presentation to ensure it fits within the allotted time (10-15 minutes).
- Focus on clear articulation, engaging delivery, and confident body language.
- Deliver Your Presentation:
- Each student/team will deliver their presentation in class on [presentation date].
- Dress professionally and use appropriate body language and eye contact.
- Engage the audience and be prepared to handle questions during the Q&A session.
Grading Rubric
| Criteria | Excellent (5) | Good (4) | Adequate (3) | Needs Improvement (2) | Poor (1) | Score |
| Introduction | Clear, engaging, and professional introduction. | Clear and professional introduction. | Adequate introduction but lacks engagement. | Incomplete or unclear introduction. | No clear introduction. | |
| Project Background | Provides a clear and concise background of the company and its sustainability initiatives. | Provides a good background but lacks some detail. | Adequate background but lacks engagement. | Incomplete or unclear background. | No clear background provided. | |
| Problem Statement | Clearly defines the problem with strong evidence. | Defines the problem with good evidence. | Defines the problem but lacks strong evidence. | Problem statement is unclear or lacks evidence. | No clear problem statement. | |
| Project Objectives and Methods | Thorough and insightful explanation of objectives and methods. | Good explanation with clear steps. | Adequate explanation but lacks detail. | Unclear or incomplete explanation. | No clear explanation provided. | |
| Budget | Detailed and justified. | Clear and reasonable. | Adequate but lacks justification. | Unclear or unrealistic budget. | No clear budget. | |
| Evaluation Plan | Specific metrics and methods for tracking progress. | Clear evaluation plan. | Adequate but lacks specificity. | Unclear or incomplete evaluation plan. | No clear evaluation plan. | |
| Conclusion | Clear and compelling summary of findings and recommendations. | Clear summary of findings and recommendations. | Adequate summary but lacks engagement. | Conclusion is unclear or lacks detail. | No clear conclusion. | |
| Q&A Session | Answers questions clearly and thoroughly, shows deep understanding. | Answers questions clearly, shows good understanding. | Adequate answers to questions, some understanding. | Incomplete or unclear answers, limited understanding. | Cannot answer questions, lacks understanding. | |
| Overall Presentation | Professional, engaging, clear speech, excellent body language. | Professional and clear, good engagement and body language. | Clear presentation but lacks engagement or professionalism. | Unclear or unprofessional delivery, needs improvement. | Poor delivery, very unclear or unprofessional. | |
| Visual Aids | Excellent use of visuals, clear, relevant, and professional. | Good use of visuals, mostly clear and relevant. | Adequate use of visuals, some relevance issues. | Limited or unclear visuals, not very relevant. | No or poor use of visuals. | |
| Total Score: ____ / 50 |
Submission Details
- Submit your presentation slides by [due date].
- Be prepared to deliver your presentation in class on [presentation date].